The need knower
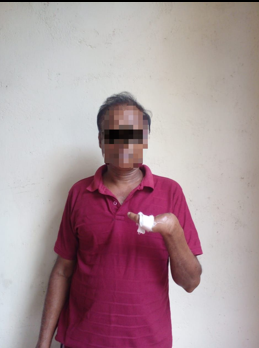
Name - Mr.Ajith Nihal
Age - 55 years old
Ajith is a dedicated farmer
Age - 55 years old
Ajith is a dedicated farmer
About need knower
Mr. Ajith Nihal has lost four fingers in his left hand due to a factory accident. Even though he does not have four fingers he is doing his primary work alone from his dominant hand. Mr. Ajith wants to contribute in his day to day activities especially in farming using both hands
Challenges Faced by the Need Knower
·
Difficulty performing farming tasks with one
hand including,
- Using a mammoty for digging and soil preparation.
- Operating a grass-cutting machine.
- Cutting branches while climbing trees.
- Tying strings and handling small objects.
Physical limitations
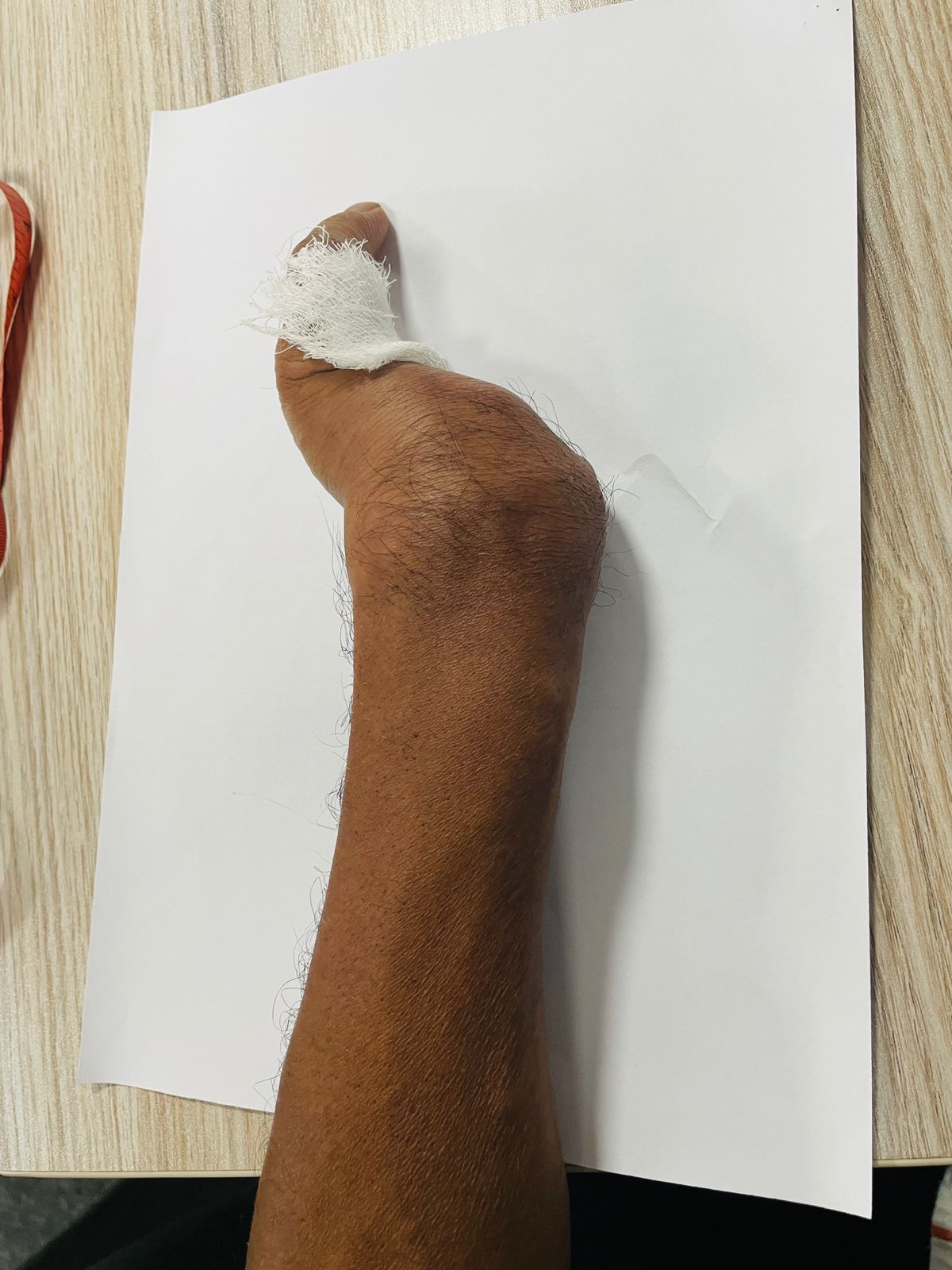
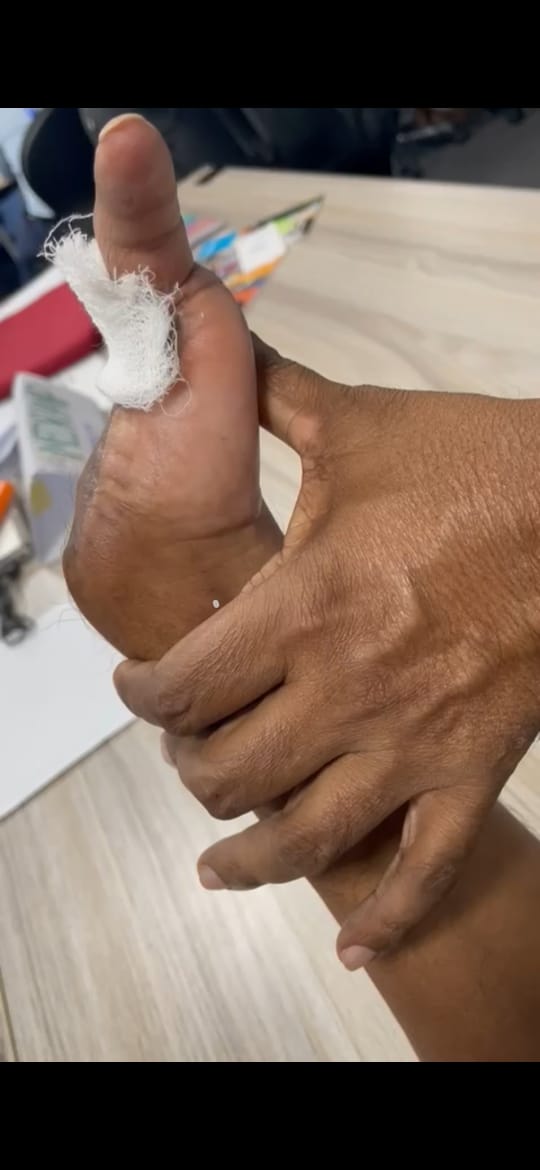
- Shaking hand(injury hand)
- Limited movement of the little finger.
- Restricted wrist mobility
Requirements of the need knower


- Should look like a real hand to avoid the need to hide it.
- He needs to get support from his left hand when holding tools with his dominant hand while farming.
- Easy to wear and remove independently.
Ideas
1.Spring-Based Finger Bending System
A design uses a spring mechanism to bend the
fingers of the prosthetic hand. Each finger has two hinges and bending the fingers using strips, but since we faced issues where to place springs , So we moved to another mechanism.
2.Hinged Finger Mechanism with Direct Bending
Design a three-fingered hand with a palm, featuring three hinges per finger for natural movement. The user can manually bend the fingers at the hinges, enabling various grip positions to support the dominant hand.
Mechanism
·
- Two mechanical hinges per finger for natural flexion.
- Manual Bending- User applies force directly to bend fingers.
- Grip Control- Manually positioned fingers offer stable object support.
Issue
Since the hinges are not stably positioned when in a gripping we moved to another mechanism
3.Twine-Based Flexible Finger Bending System With Hinges
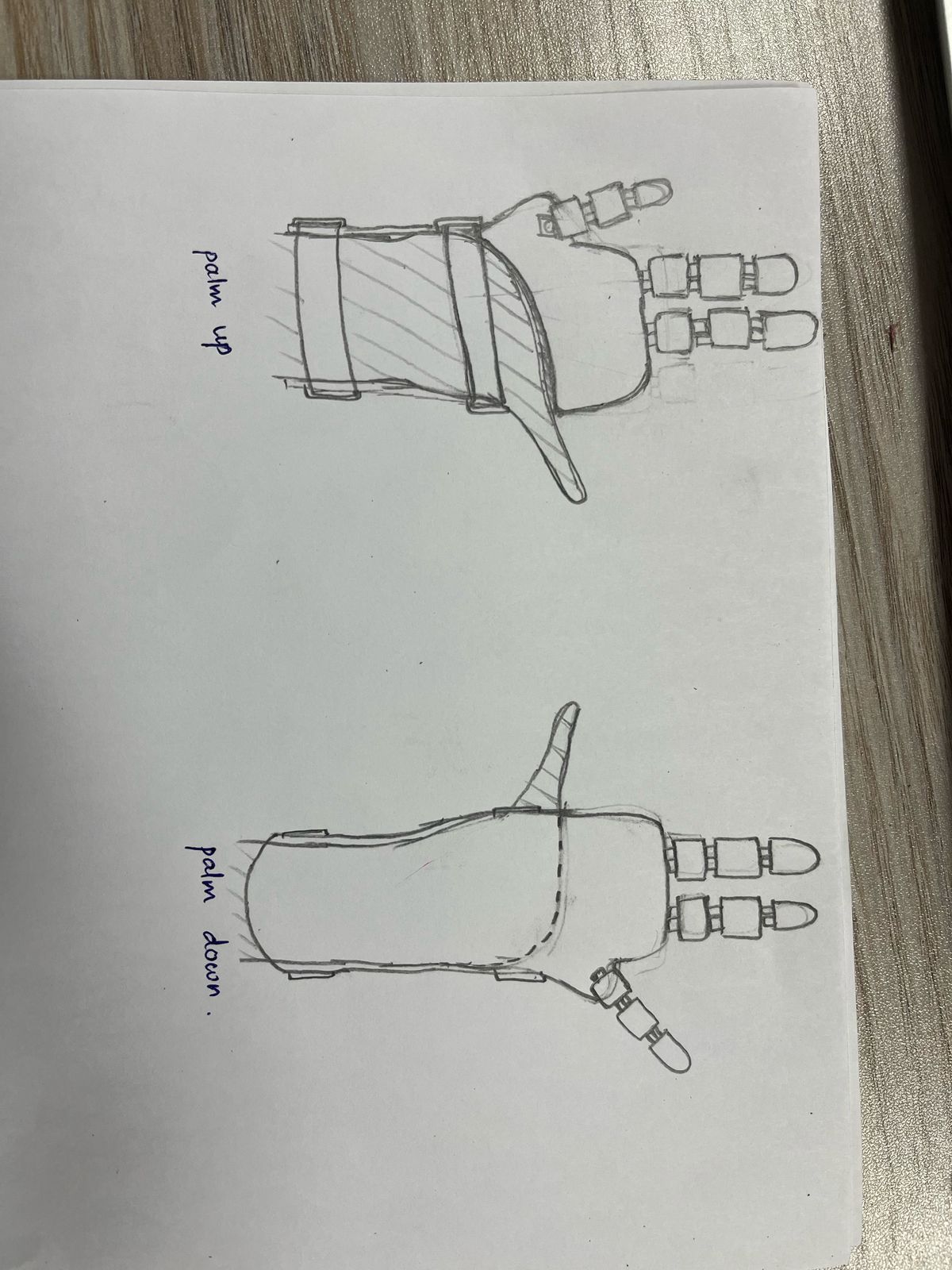
Twine strips are integrated into the fingers to
provide flexibility. Each finger has two hinges, and when tension is
applied to the twine from other hand by pulling the strip, the fingers bend directly at the hinges to grip objects.
Mechanism
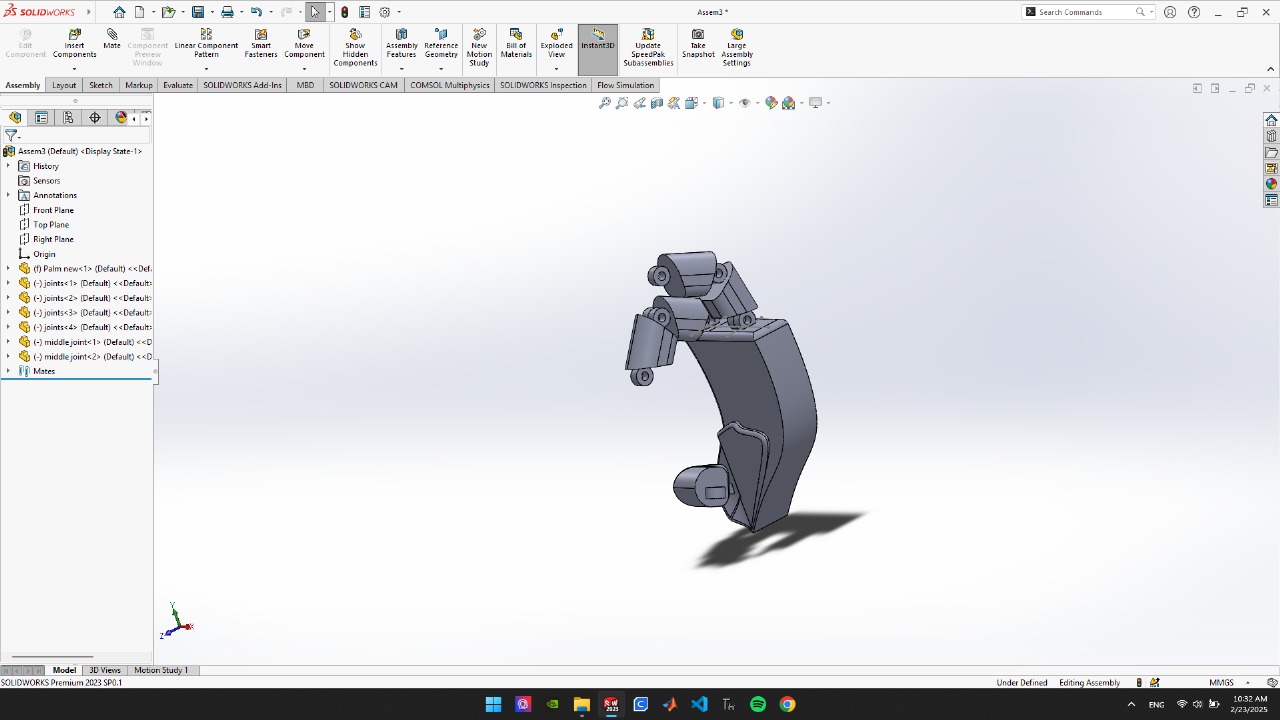
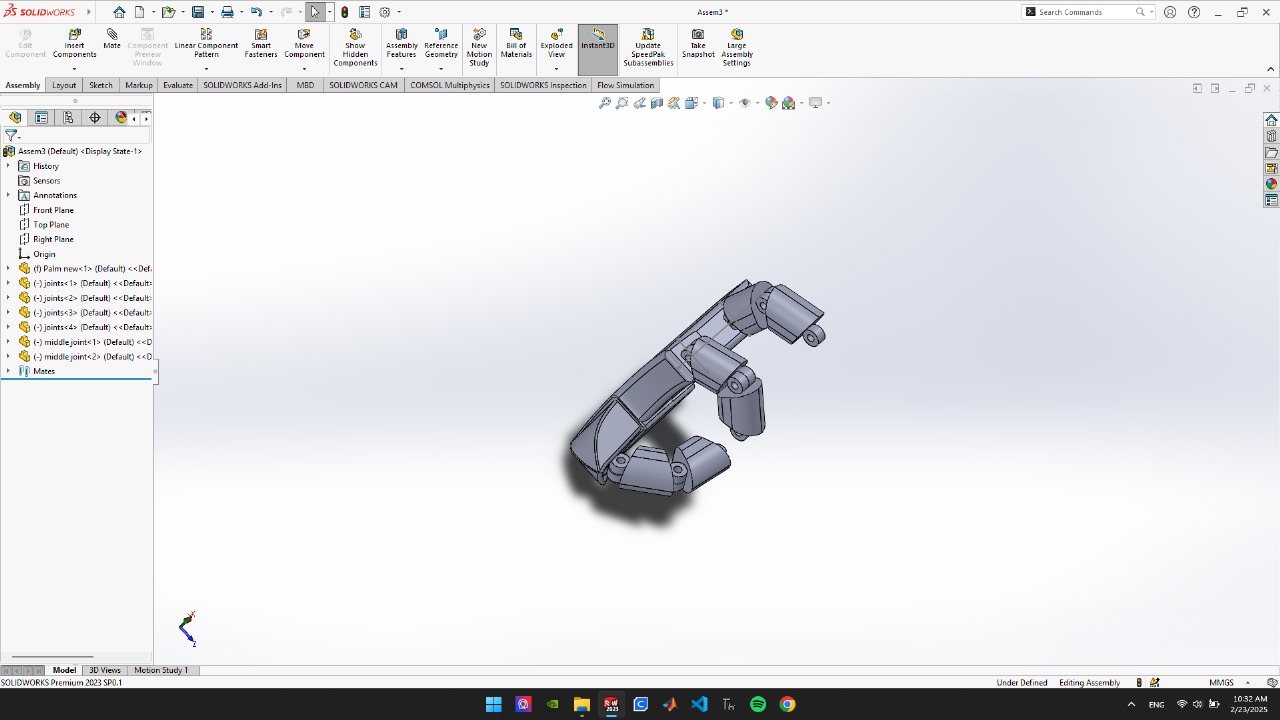

- Two hinges in each finger provide direct bending.
- Twine strips are placed inside the finger.
- By pulling the straps causes fingers to bend the desired level user can grip objects.
- All the straps are connected to the forearm proximal to the wrist.
Issues

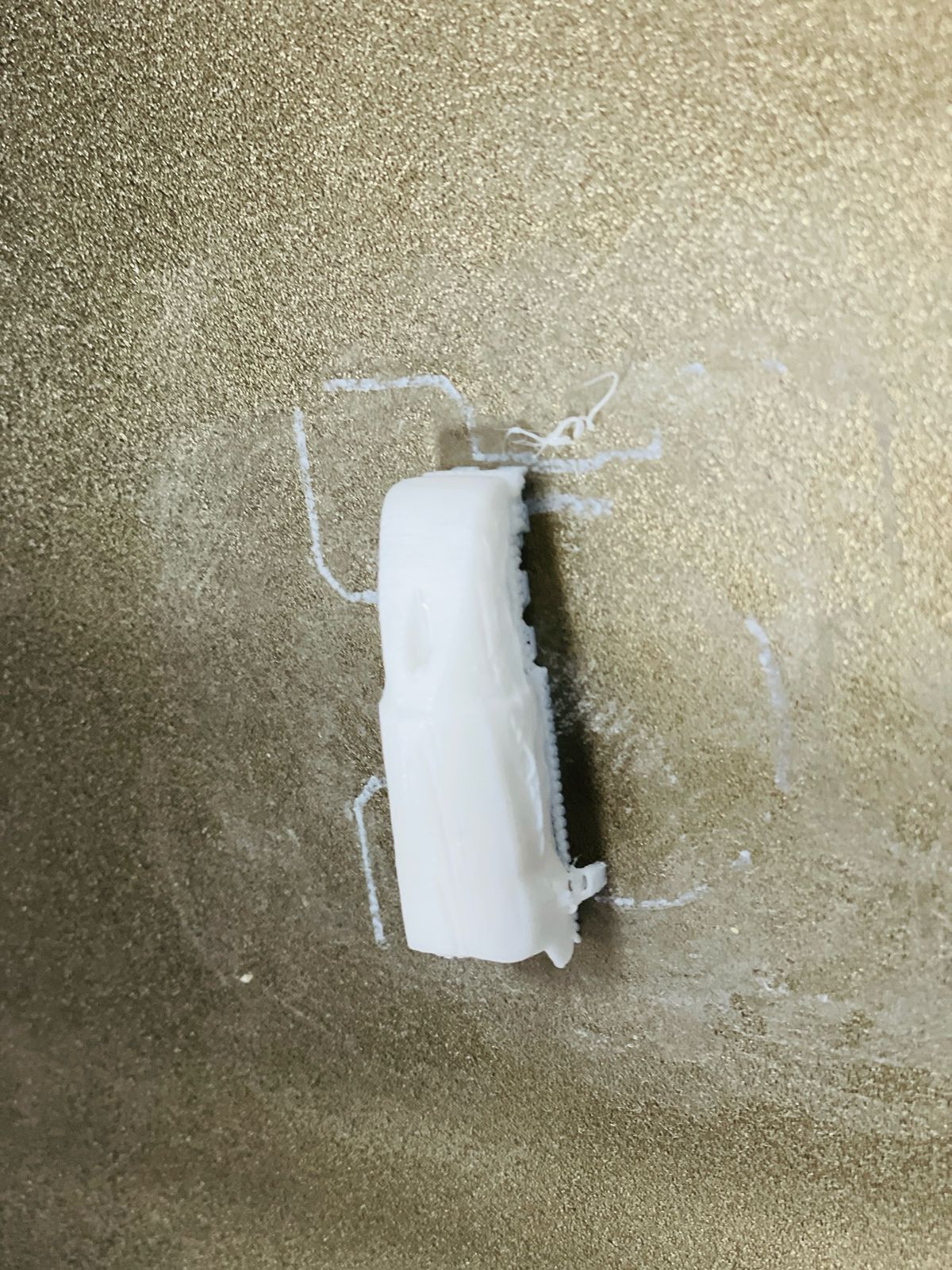
After we did the 3D printing of hinges and finger digits, we tried to assemble the fingertips using hinges, but there, some hinges and finger digits were broken when we tried to send hinges through the finger digits and assemble the fingertips.
4.Twine Based Flexible Finger Bending System Using Zip Lines
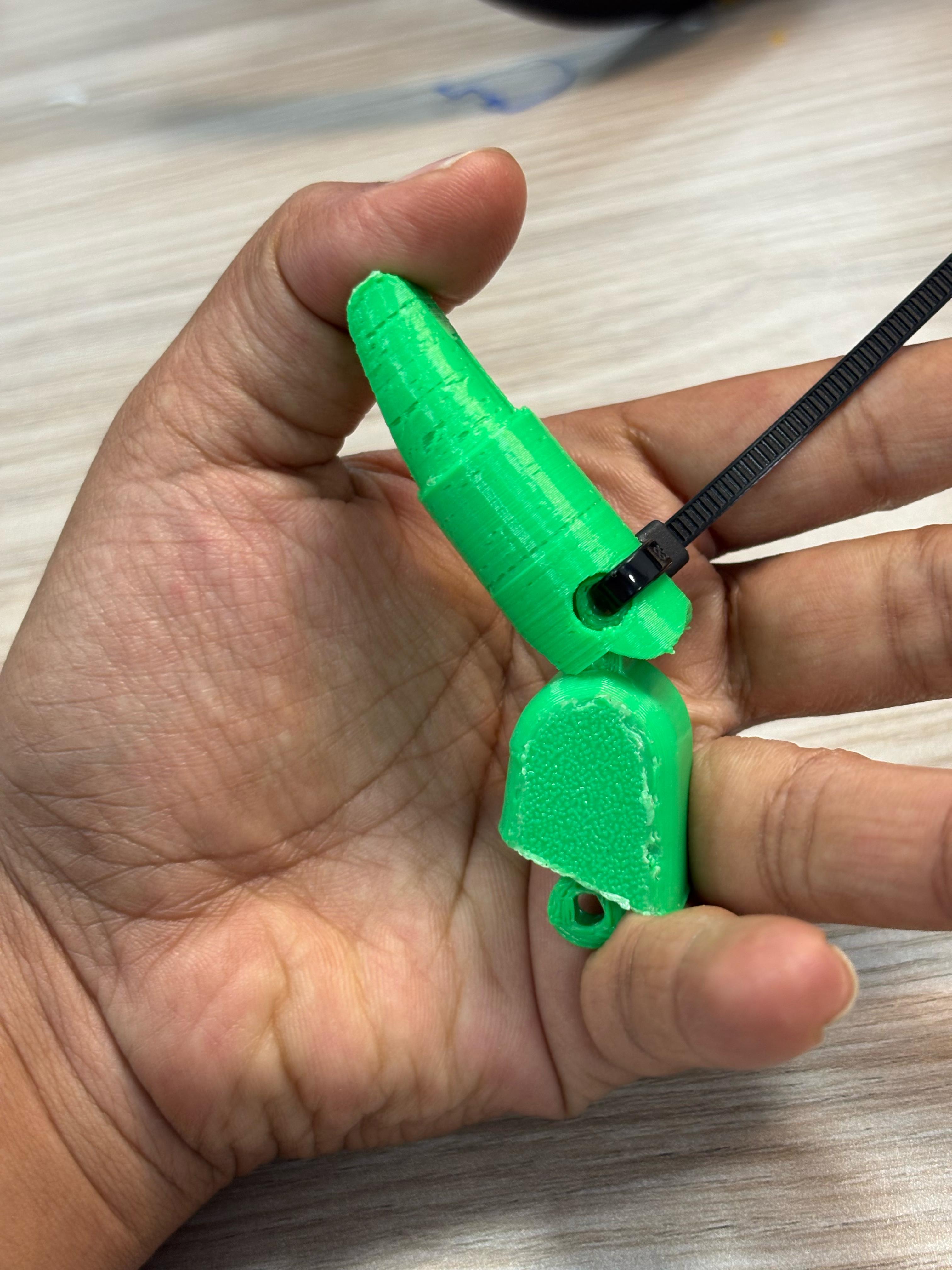
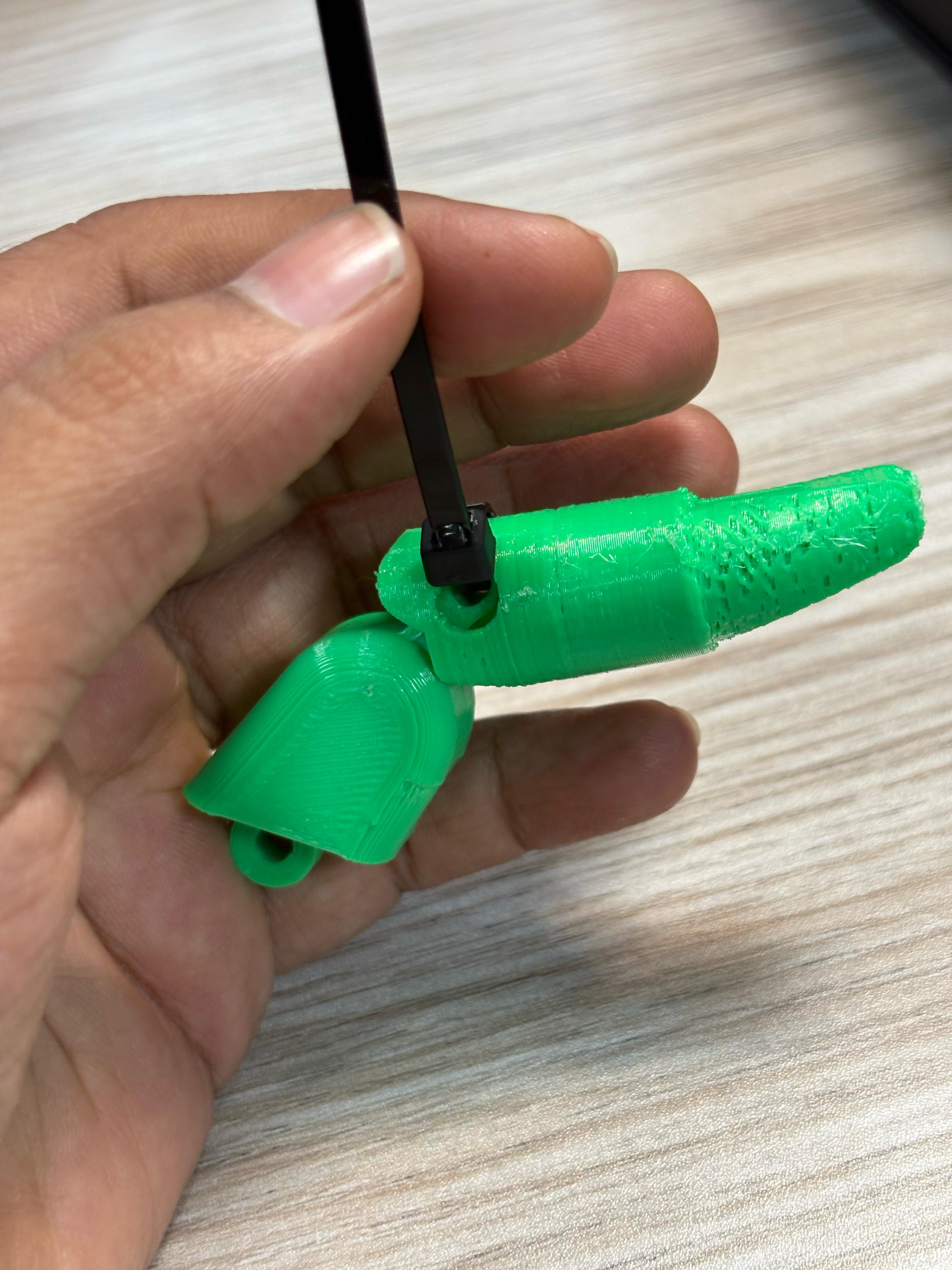


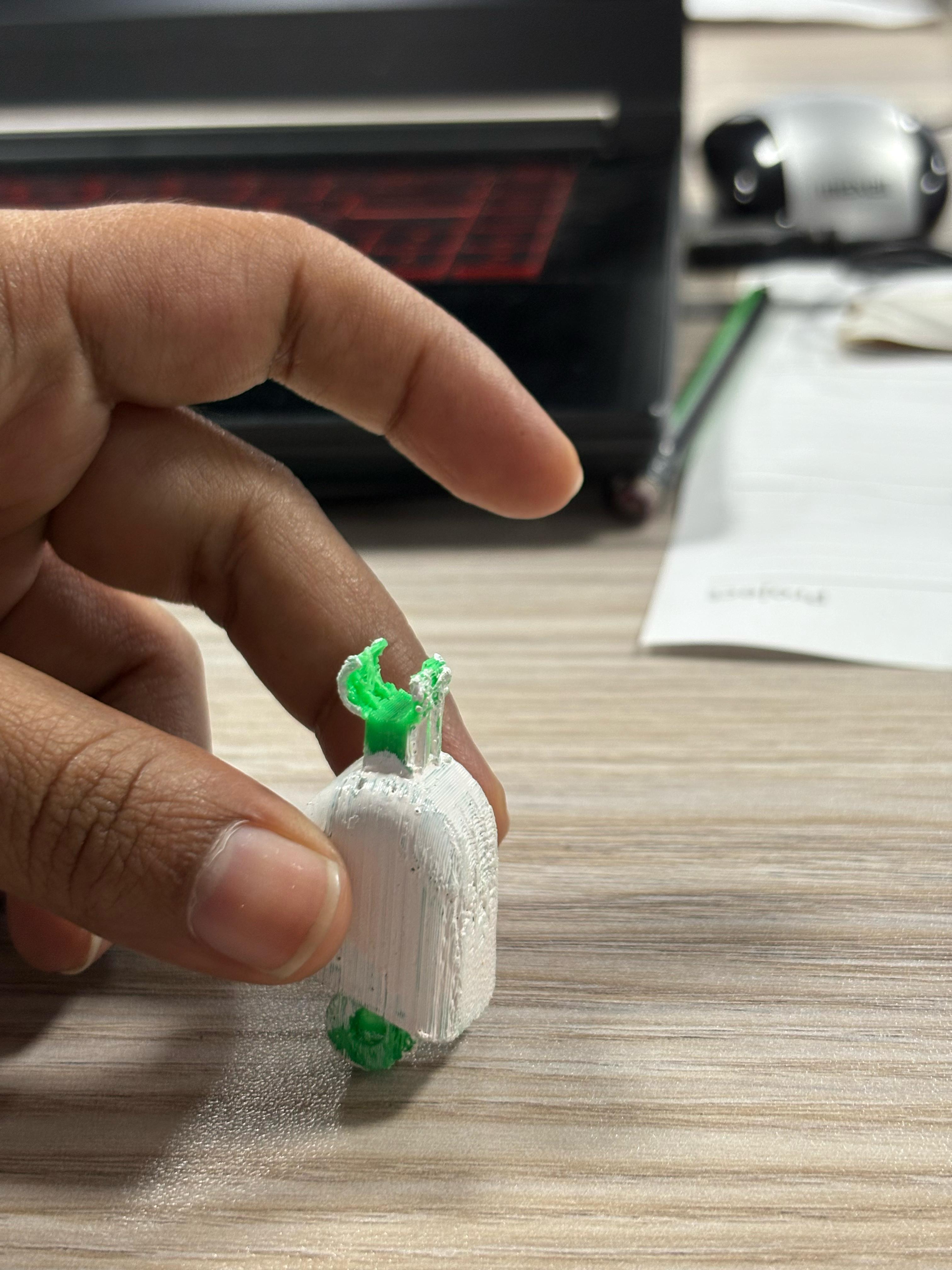
So here instead of hinges, we use zip lines to connect the digits and bend the fingers which are easy of use and cost-effective. This costs only Rs.3($0.009 ) in the Sri Lankan market.
Mechanism
- The two zip lines in each finger connect the finger digits and allow direct bending.
- Twine strips are placed inside the finger.
- By pulling the straps causes fingers to bend to the desired level so the user can grip objects.
- All the straps are connected to the forearm proximal to the wrist.
Prototyping
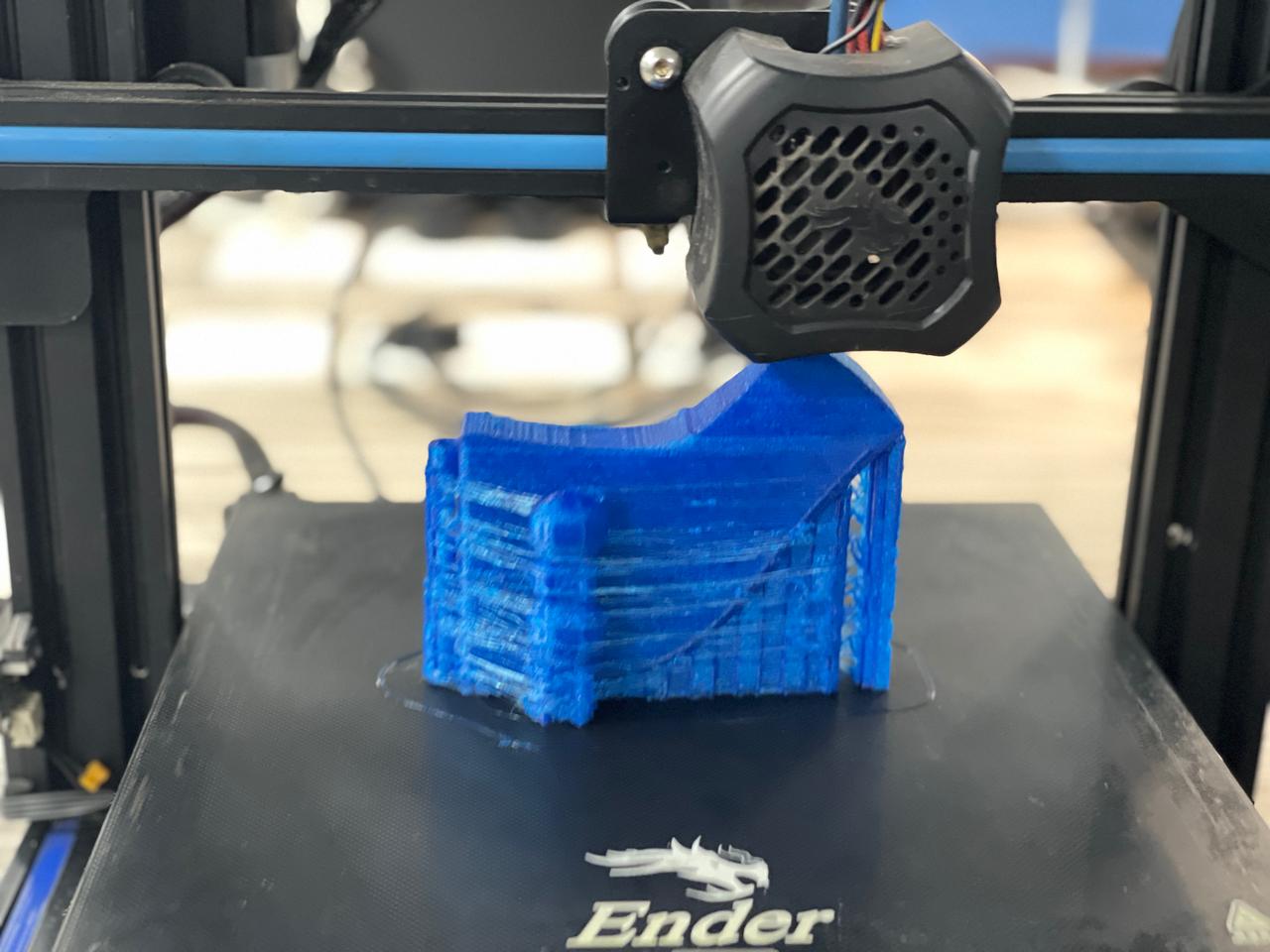
Phase 1-3D Printing Finger Digits and Assembly
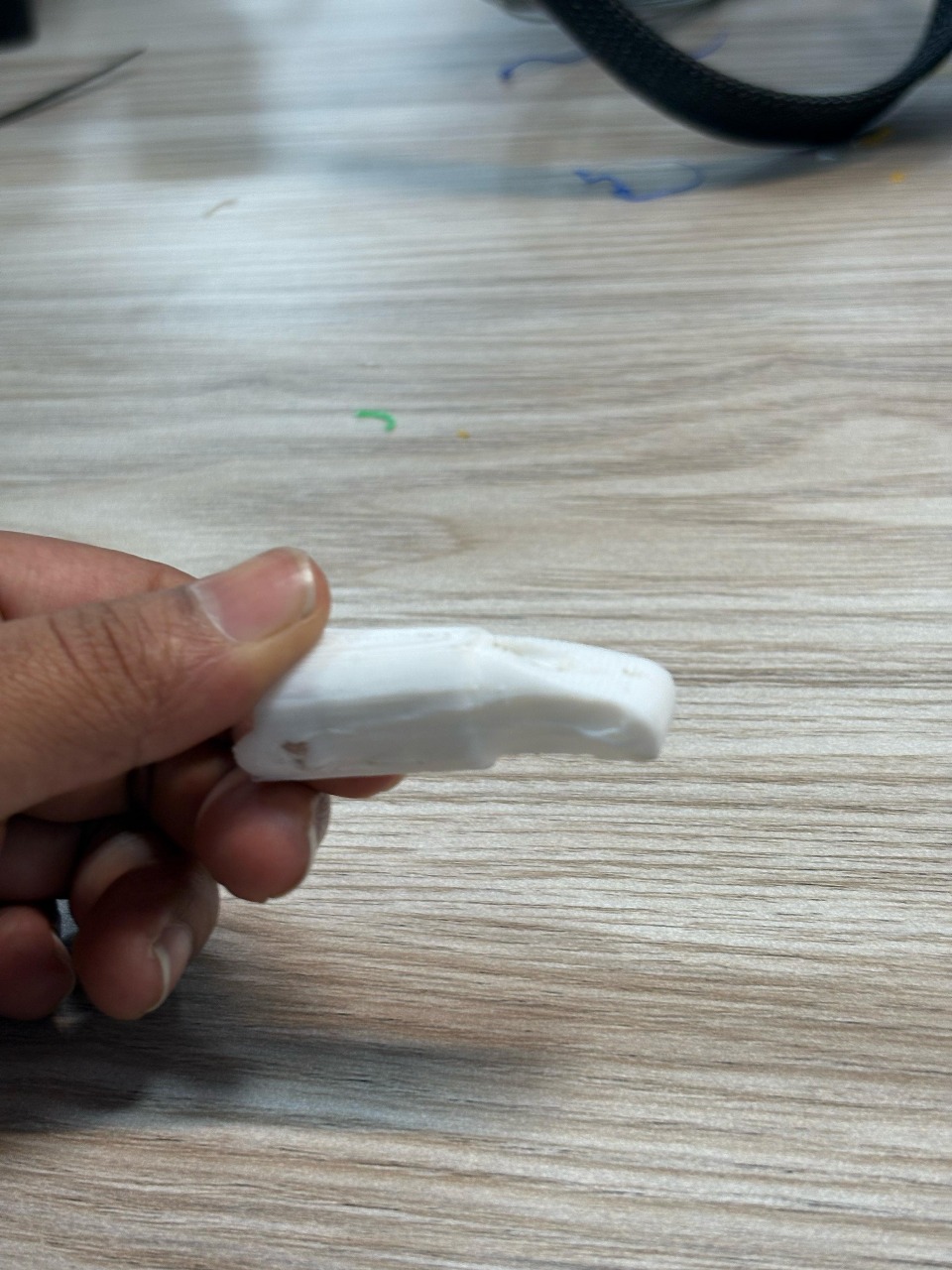


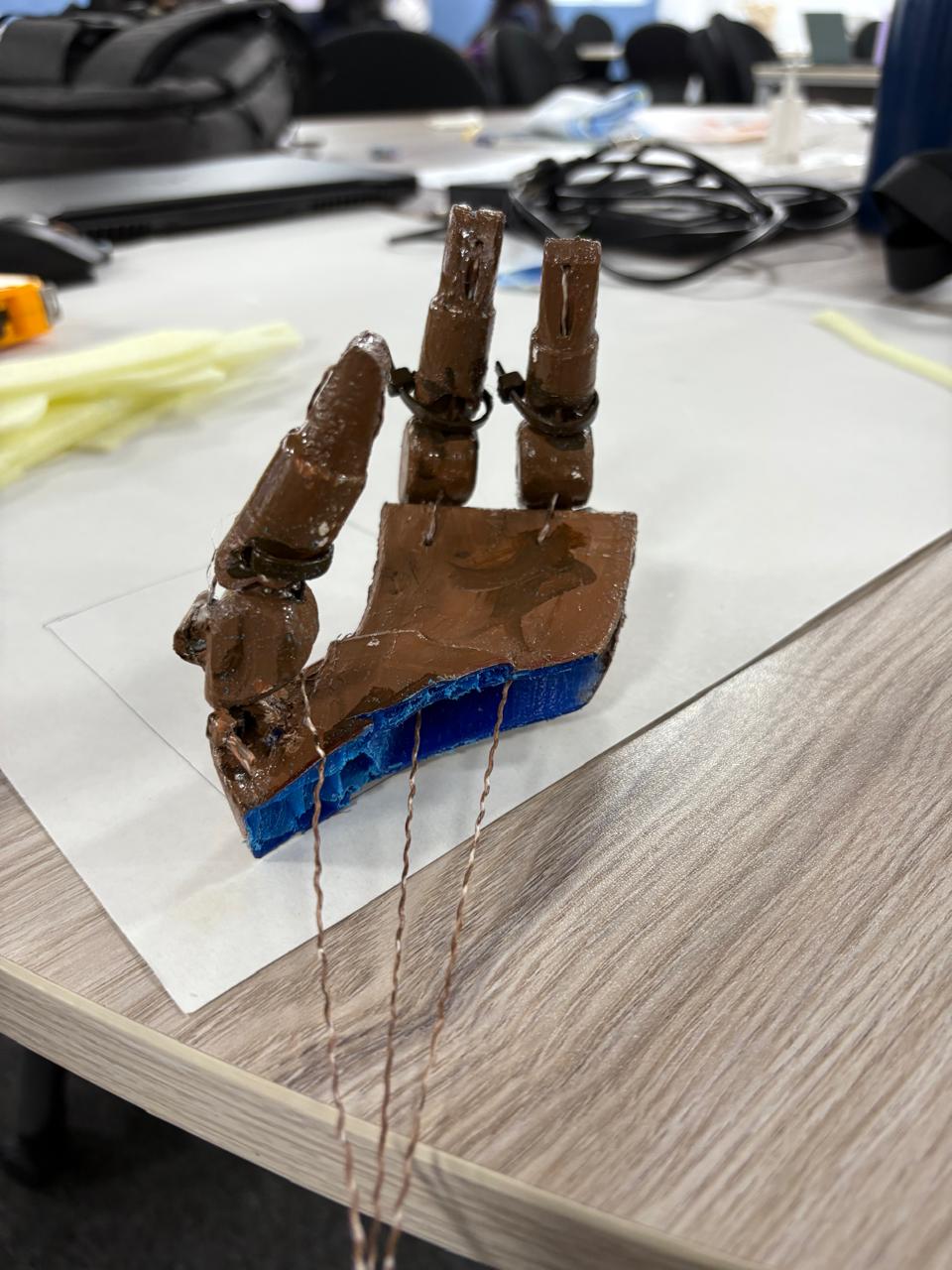
Designed 3D finger digits with two segments for durability and flexibility using lightweight PLA filament. Connected segments with zip lines and tested strength and flexibility. Developed functional thumb, index, and middle finger tips for tool grasping.thumb finger tip index , middle
Phase 2- Twine Strap Input for Finger Control
Input twine straps through hollow finger sections. Extend twine outwards to control finger bending and straightening. Pulling the twine should mimic natural finger curling. Use a simple pull-and-release mechanism for ease of use. Choose strong, weather-resistant twine for outdoor durability.
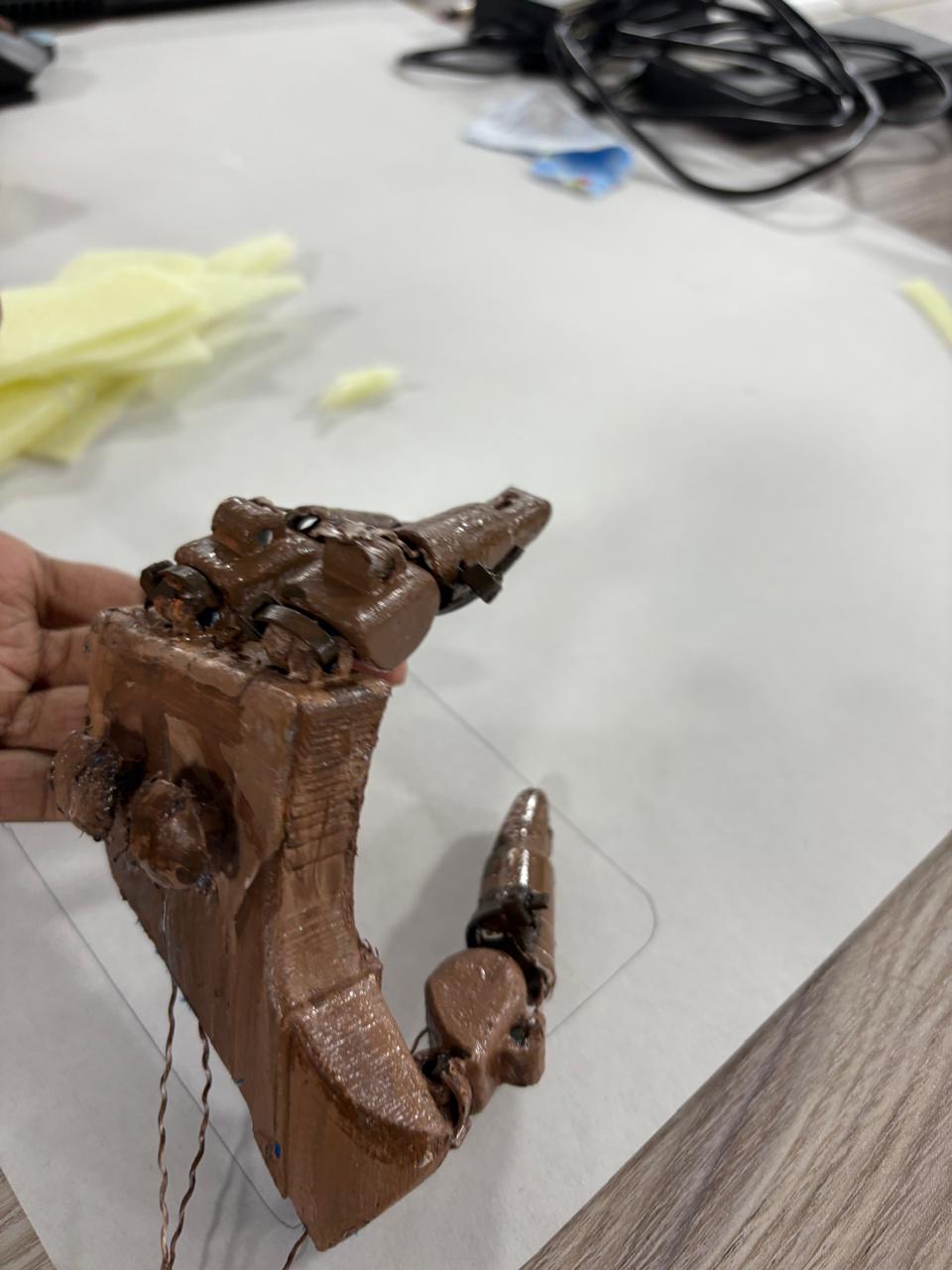
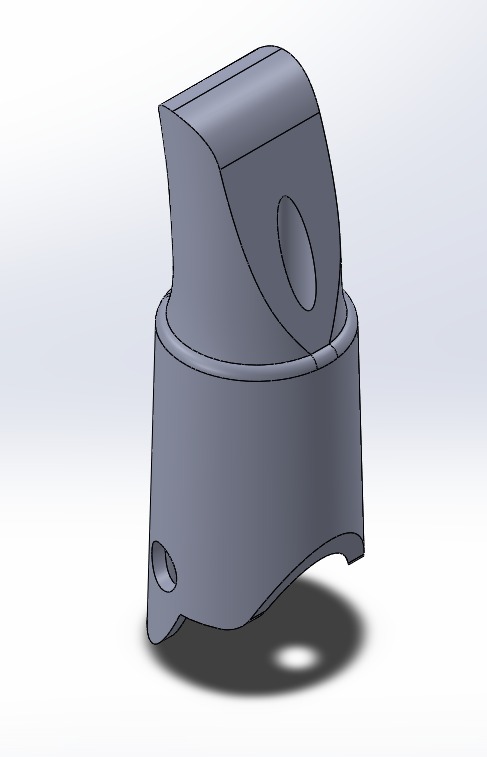
Phase 3 - 3D printing the palm
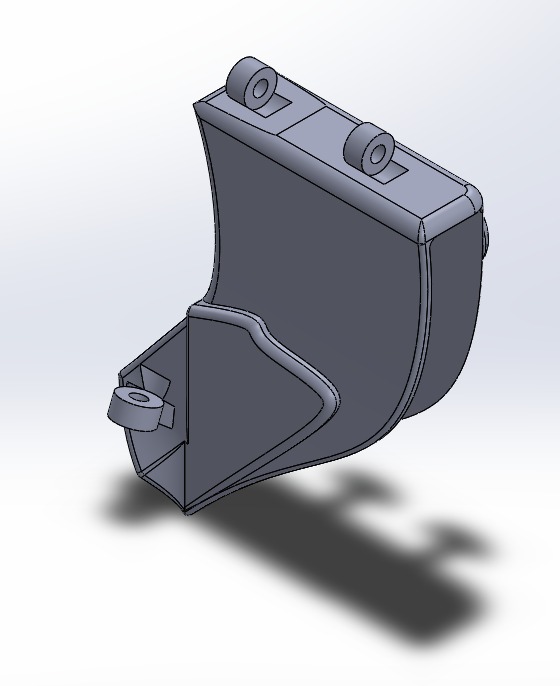
Designed a robust, ergonomic palm structure using TPU to support finger attachment. Palm include secure slots for zip lines . Ensure a cushioned or shaped inner surface for comfort. Provide sufficient surface area for a firm grip on tools like a mammoty or grass cutter.
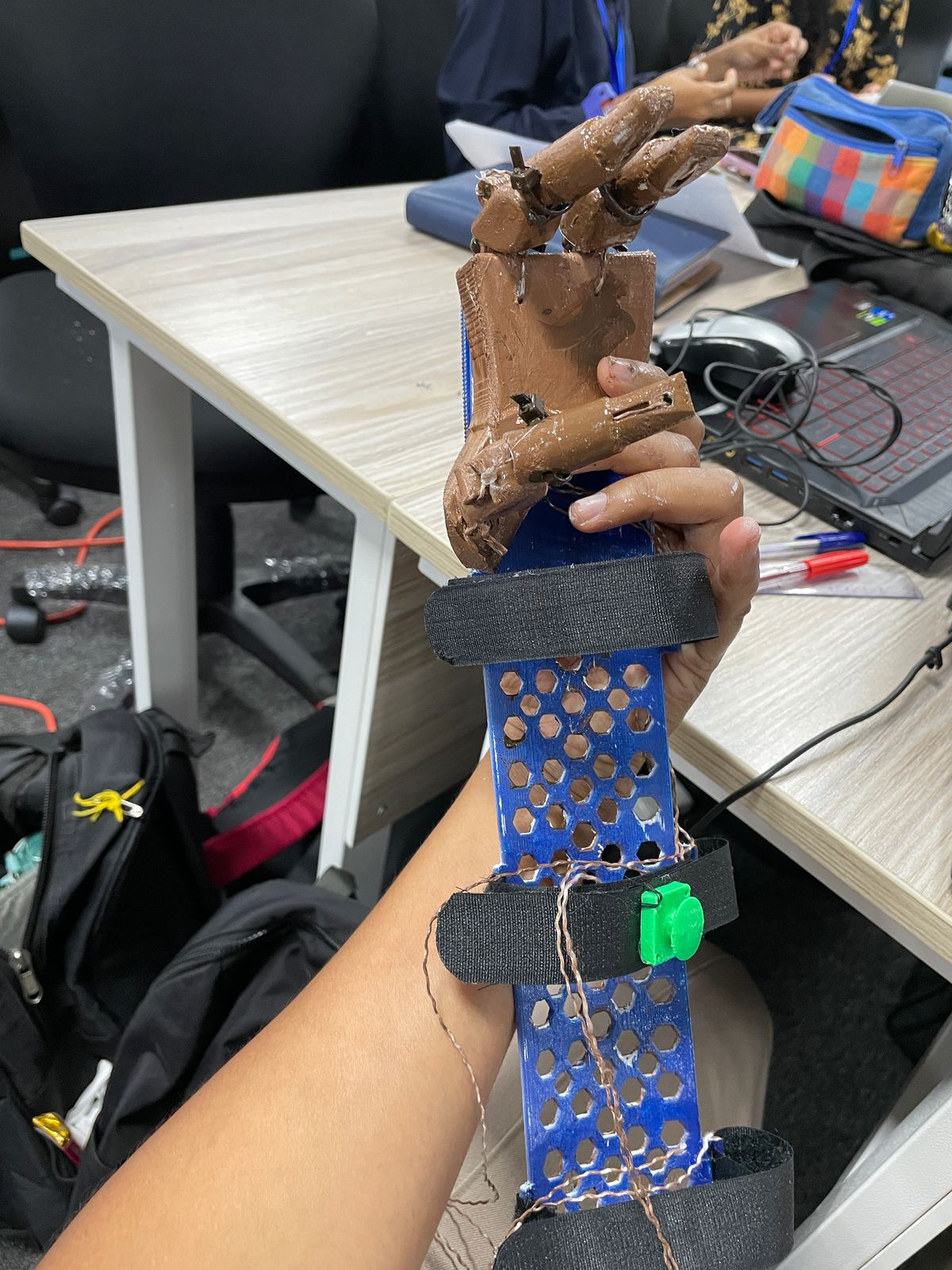
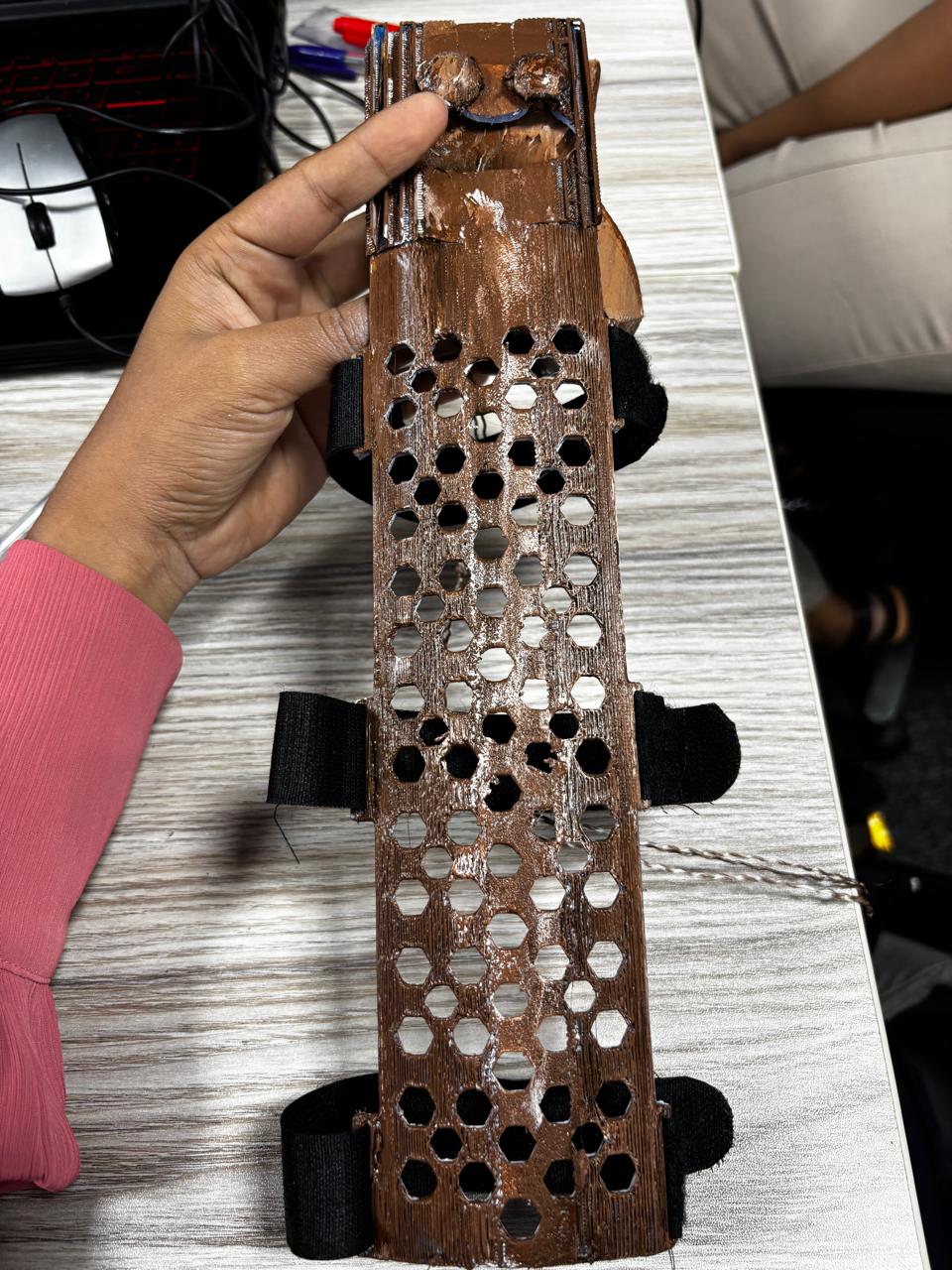
Phase 4: Designing the Back Arm Guard
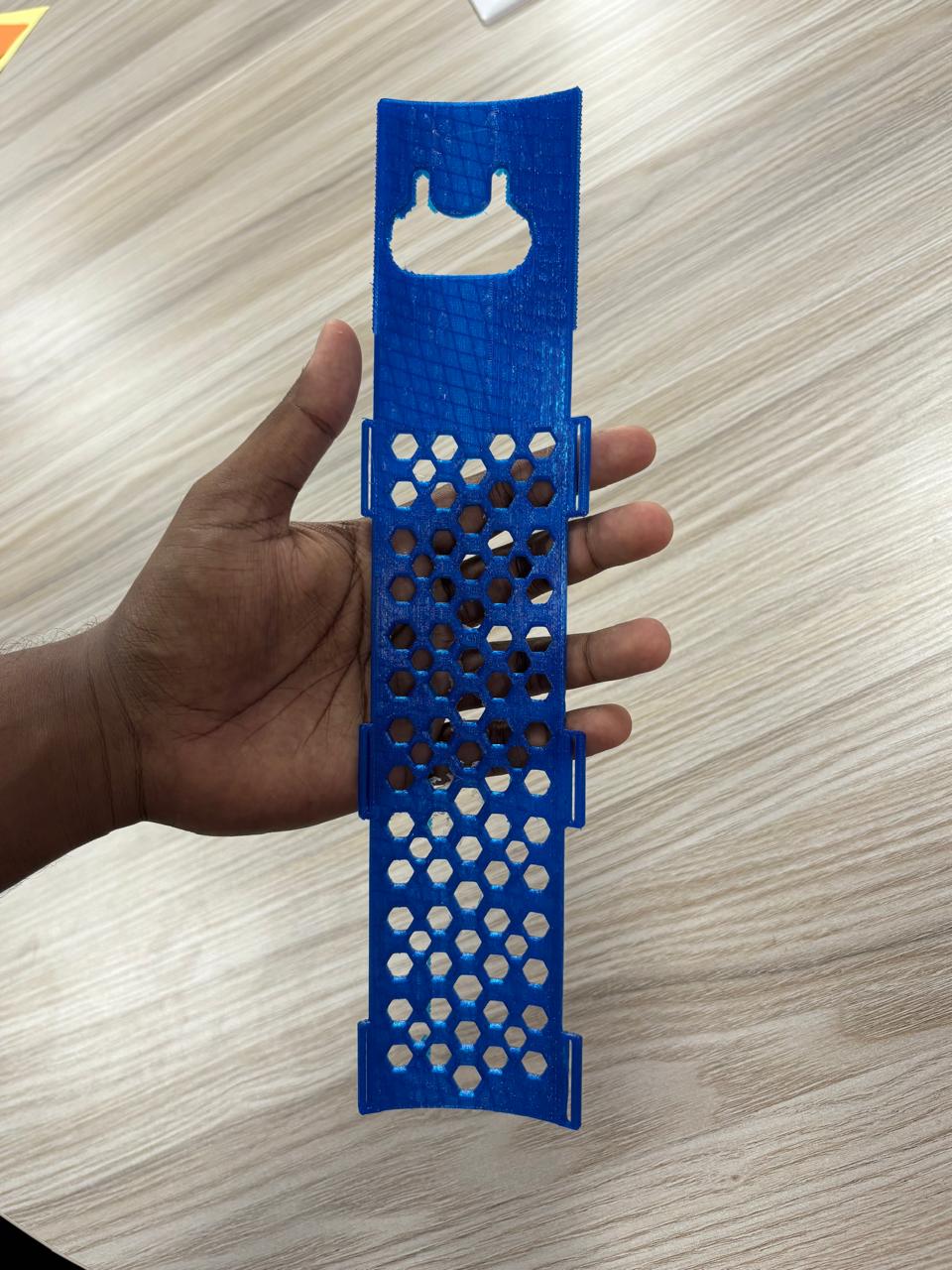

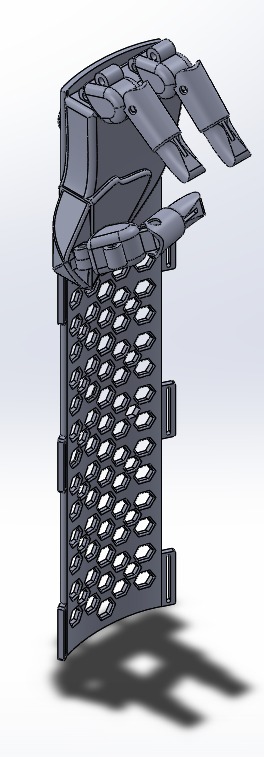
Provide stability and support for the prosthetic hand using lightweight, TPU 3D design. Designed a mesh-like arm guard for comfort and efficiency. Cover the forearm with adjustable strapping. Forearm plate with velcro strap control and ensure protection from friction and pressure.
Phase 5 - Designed a Thread bob
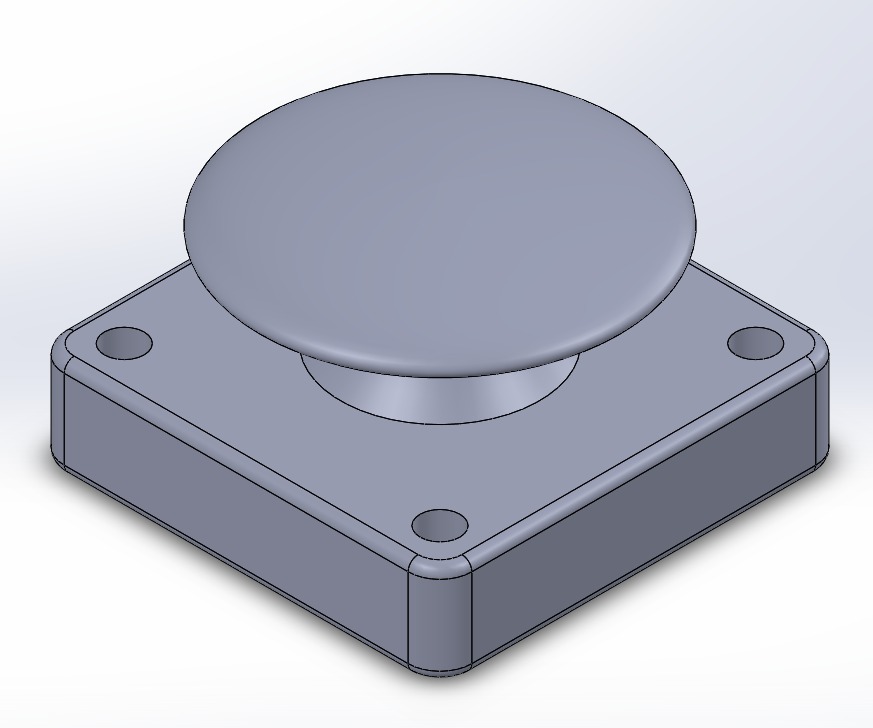
The threaded bob secures the twine strap, ensuring stability and precise finger movement. It allows tension adjustments, improves grip control, and distributes force evenly, enhancing durability and reliability.
Phase 6 - Middle Joints of Fingers
The middle joints of fingers add an extra digit and more hinge support for the fingers .middle joint
Future Advancements
1.Convert to an electronic hand using servo motors.
2.Match hand color to the user’s exact skin tone.
Final Product



